When your facility loses power, every second counts. Whether you’re running a hospital, a data center, or a manufacturing plant, your backup power system isn’t just infrastructure—it’s a lifeline. That’s why choosing the right diesel generator manufacturer might be one of the most critical decisions you’ll make for your operation.
I’ve spent over fifteen years consulting on power systems, and I’ve seen what happens when organizations rush this decision. I’ve watched facilities struggle with generators that fail during load tests, manufacturers that vanish when you need parts, and “bargain” units that cost triple their sticker price in repairs. The stakes are too high to get this wrong.
What Is a Diesel Generator Manufacturer and Why Does It Matter?
A diesel generator manufacturer is a company that designs, engineers, and produces complete power generation systems—integrating diesel engines, alternators, control systems, and enclosures into turnkey solutions. But here’s what most people miss: not all manufacturers are created equal.
Some manufacturers build everything in-house. Others assemble components from various suppliers—pairing a Perkins engine with a Stamford alternator and their own control panel, for example. Some specialize in industrial diesel generators for mission-critical applications, while others focus on portable or residential units.
The manufacturer you choose determines your generator’s reliability, fuel efficiency, service availability, parts supply, warranty coverage, and ultimately, your total cost of ownership over 20+ years. It’s not just about buying a machine; you’re entering a long-term relationship.
Let me walk you through the factors that separate exceptional manufacturers from the rest.
Evaluating Manufacturer Reputation and Track Record
Start with reputation, but dig deeper than marketing claims. A manufacturer’s track record tells you how they’ll perform when you need them most.
Look for industry tenure and project history. Manufacturers with 20+ years in business have weathered market cycles, refined their designs, and built institutional knowledge. Ask potential manufacturers for case studies in your industry. If you’re running a hospital, you want to see successful installations in healthcare facilities that faced similar regulatory and uptime requirements.
Check references and site visits. Don’t just read testimonials—call them. Ask about commissioning experiences, warranty responsiveness, and unplanned maintenance. Better yet, request site visits to see generators in operation. Brands like Tesla Power often facilitate these visits because they understand that seeing is believing.
Review certifications and compliance. Reputable manufacturers maintain third-party certifications—ISO 8528 standards for generator sets, ISO 9001 for quality management, and regional emissions compliance (EPA Tier 4, EU Stage V). These aren’t just badges; they represent audited processes and consistent quality control.
I once consulted for a pharmaceutical plant that skipped this step. They bought from a manufacturer with impressive specs but no ISO certifications. When the generator failed validation testing, the manufacturer blamed “installation issues.” It took 11 months and $180,000 in legal fees to resolve. That’s a lesson you don’t want to learn firsthand.
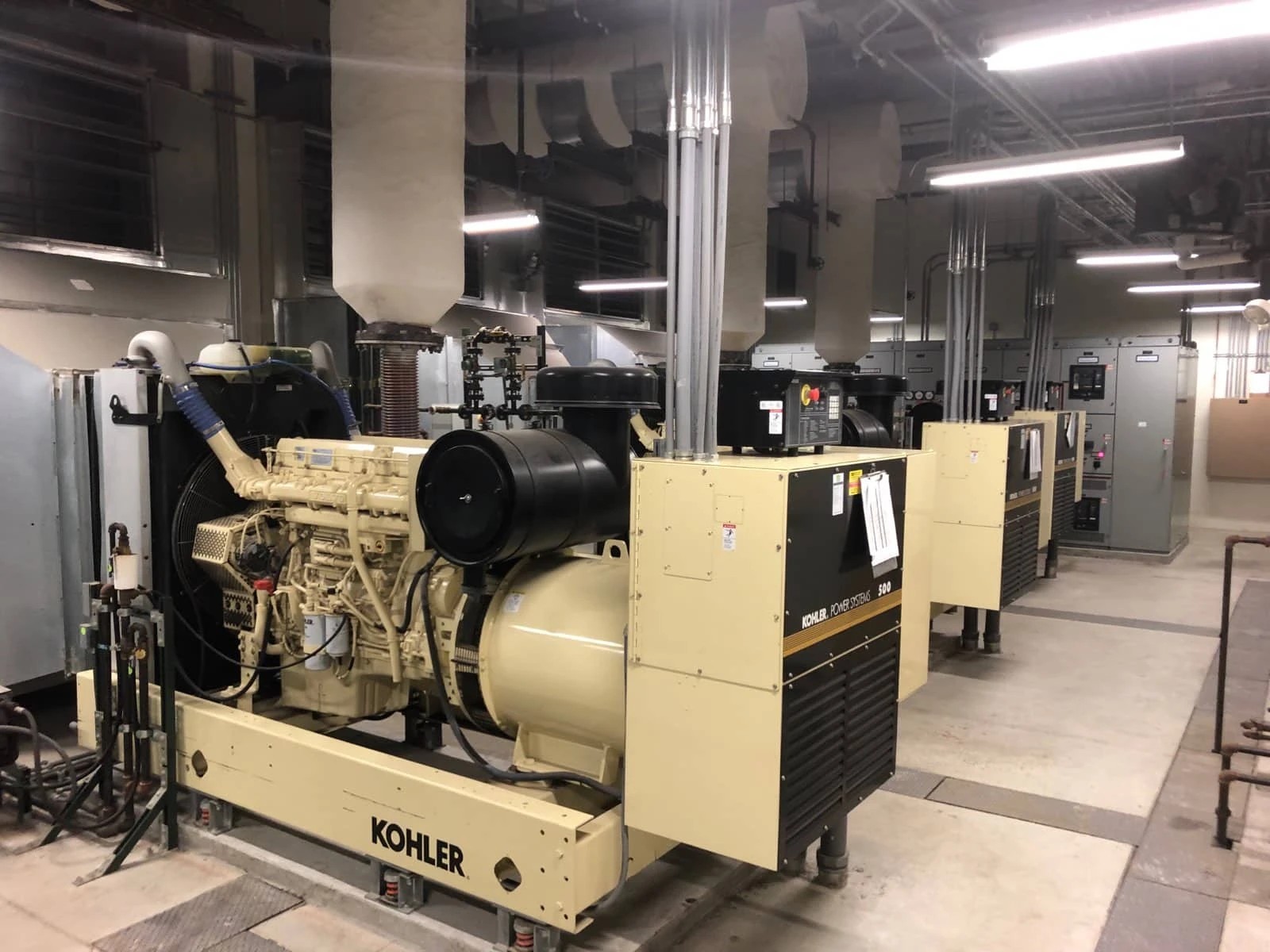

Engine and Alternator Quality: The Heart of Your Generator
The engine and alternator are your generator’s core components, and manufacturer choices here profoundly impact performance and longevity.
Engine brands matter—a lot. Top-tier diesel genset manufacturers partner with proven engine brands: Perkins, Cummins, Volvo Penta, MTU, and Deutz. These engines come with extensive field data, global parts networks, and predictable maintenance schedules. When a manufacturer uses these engines, they’re leveraging decades of refinement.
But here’s a nuance: don’t just look at the engine brand—look at the application engineering. A great engine poorly matched to your load profile or improperly integrated will underperform. Ask manufacturers how they configure governor systems, cooling capacity, and fuel delivery for your specific duty cycle (prime, standby, or continuous).
Alternator selection is equally critical. Stamford, Leroy Somer, and Marathon are industry standards for power generation equipment, delivering clean power with minimal harmonic distortion. The alternator’s voltage regulation, temperature rise characteristics, and overload capacity determine how well your generator handles inrush currents when motors or transformers start.
I worked with a data center that learned this the hard way. Their generator featured a reputable engine but a generic alternator with poor voltage regulation. During UPS transfers, voltage sag crashed servers. They ended up retrofitting a Stamford unit at 3x the original alternator cost.
Integration expertise separates good manufacturers from great ones. The best manufacturers don’t just bolt components together—they optimize the entire system. They match engine torque curves to alternator load acceptance. They engineer airflow for consistent cooling. They design control systems that respond intelligently to transient loads.
Manufacturers like Tesla Power invest heavily in this integration work, which is why their generators often outperform spec-sheet competitors in real-world conditions.
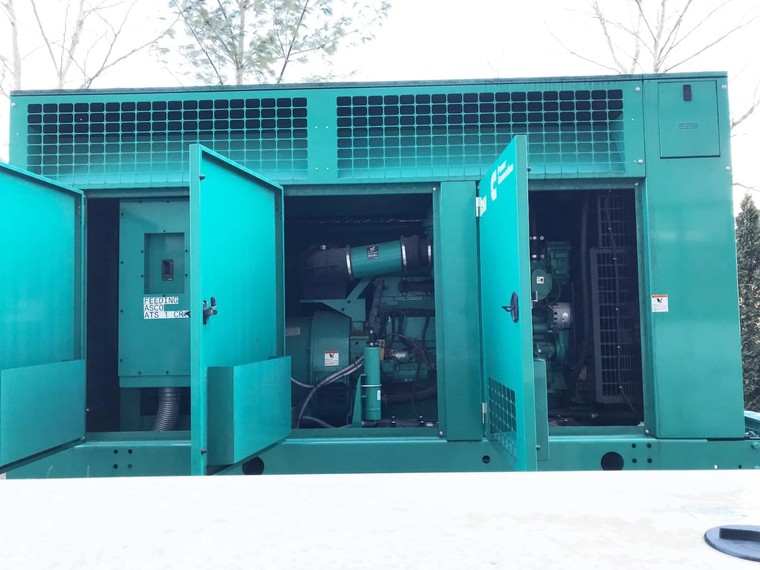

Service Network and Parts Availability
Your generator will need maintenance and eventually repairs. The manufacturer’s service network determines whether that takes hours or months.
Geographic coverage is non-negotiable. If you’re in Denver and your manufacturer’s nearest service center is in Miami, you’re in trouble. Map out where the manufacturer has factory-trained technicians, authorized service partners, and parts depots. For critical facilities, look for manufacturers offering on-site emergency support contracts.
Parts availability can make or break uptime. Here’s what to verify:
- Stocking levels: Does the manufacturer warehouse commonly replaced parts (filters, belts, fuel injectors) regionally, or does everything ship from overseas?
- Lead times: What’s the standard delivery time for consumables versus major components (turbochargers, engine blocks)?
- Obsolescence policy: Will parts remain available for 15-20 years, or will your generator become unsupportable when the manufacturer launches a new model line?
I’ve seen facilities struggle when their generator manufacturer went through acquisition or restructuring. Suddenly, parts that arrived in 48 hours took 12 weeks—or weren’t available at all. This is why many procurement teams favor manufacturers with vertically integrated supply chains and long-term parts availability guarantees.
Technical support quality varies wildly. Test this before you buy. Call the support line. Ask detailed technical questions about load factor derating, paralleling configurations, or emissions compliance. Do you reach knowledgeable engineers, or tier-one call centers reading scripts? The best manufacturers provide direct access to application engineers who can troubleshoot complex issues.
Training and documentation matter too. Comprehensive manuals, online training modules, and on-site commissioning support help your team operate and maintain the generator correctly, reducing nuisance callouts and extending equipment life.

Compliance Standards and Emissions Regulations
Regulatory compliance isn’t optional, and it’s getting more complex. Your manufacturer needs to navigate these requirements seamlessly.
Understand emissions tiers. In North America, EPA Tier 4 regulations cap nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM). Europe’s Stage V standards are even stricter. Some manufacturers meet these with selective catalytic reduction (SCR) or diesel particulate filters (DPF)—both require maintenance and add complexity. Others use advanced combustion strategies to comply without aftertreatment.
Ask manufacturers: What emission tier does this generator meet? How does the compliance strategy affect fuel consumption, maintenance frequency, and operating costs? Don’t assume all Tier 4 generators are equal—implementation quality varies.
Building codes and installation standards create additional requirements. NFPA 110 governs emergency backup power systems in life-safety applications. ISO 8528 defines generator performance classes. UL 2200 certifies stationary engine generators. Local jurisdictions may have noise ordinances (dBA limits at property lines) or setback requirements.
A competent manufacturer understands these regulations and designs generators that simplify compliance. They provide documentation packages—emissions certificates, sound test reports, compliance declarations—that smooth permitting and inspection processes.
I consulted for a logistics company that bought generators online from a “budget-friendly” manufacturer. When the local authority having jurisdiction (AHJ) inspected, the units lacked UL listing and emissions documentation. The facility couldn’t receive occupancy permits until they replaced the generators—a $420,000 mistake.
Future-proofing matters too. Regulations tighten over time. Some manufacturers design with headroom—engines that can meet next-generation standards with software updates or minor hardware changes. Others require complete replacement when rules change. Factor this into your decision if you plan 15+ year operating life.
Fuel Efficiency and Operating Costs
Purchase price is just the beginning. Fuel costs over a generator’s lifespan often exceed the initial investment several times over.
Fuel consumption varies significantly by manufacturer and load profile. Expect modern industrial diesel generators to consume roughly:
- 0.28-0.30 gallons per kWh at 100% load
- 0.30-0.35 gallons per kWh at 75% load
- 0.38-0.45 gallons per kWh at 50% load
But these are averages. Premium manufacturers achieve 5-10% better efficiency through optimized combustion, advanced governors, and reduced parasitic losses. Over 20 years, that difference adds up. For a 500 kW generator running 200 hours annually at 75% load (75,000 kWh/year), improving from 0.33 to 0.30 gal/kWh saves 2,250 gallons per year. At $4/gallon, that’s $9,000 annually—$180,000 over the generator’s life.
Load factor efficiency is crucial. Many standby generators operate at partial load during testing and brief outages. Manufacturers that maintain high efficiency at 50-75% load deliver real-world savings. Ask for full-load and part-load fuel curves, not just nameplate numbers.
Maintenance intervals affect total cost of ownership. Generators with longer oil change intervals (500 vs. 250 hours) or extended major overhaul schedules (30,000 vs. 20,000 hours) reduce lifecycle maintenance costs. But verify these intervals are realistic—some manufacturers overstate capabilities to improve marketing claims, leading to premature failures.
Other operating factors include:
- Cold-start reliability: Does the generator require block heaters or frequent exercising in cold climates, adding energy costs?
- Cooling system efficiency: Oversized or poorly designed radiators consume more fan power.
- Control system intelligence: Advanced controllers optimize idle speeds and load management, reducing fuel burn during low-demand periods.
Brands like Tesla Power publish detailed fuel consumption data across load ranges and offer lifecycle cost calculators—transparency that helps you make informed decisions.
Warranty Coverage and Support Terms
Warranties reveal how much confidence a manufacturer has in their product—and how much financial risk you’re assuming.
Standard warranties typically cover 1-2 years or 2,000-3,000 operating hours, whichever comes first. But read the fine print:
- What’s covered? Engine? Alternator? Control panel? Does it include labor, or just parts?
- What voids the warranty? Unapproved maintenance? Using non-OEM parts? Operating outside rated parameters?
- What’s the claim process? Do you need pre-approval for repairs, or can local technicians proceed and invoice later?
Extended warranty options vary in value. Some manufacturers offer 5-year/5,000-hour extended coverage that costs 6-8% of generator price but covers major component failures. Others offer “extended warranties” that are really just service contracts with parts discounts. Understand exactly what you’re buying.
Look for comprehensive support beyond warranty. The best diesel generator manufacturers offer:
- Commissioning services: Factory technicians supervise installation, perform startup, and train your team.
- Preventive maintenance contracts: Scheduled servicing that keeps generators in peak condition and preserves warranty coverage.
- Emergency repair guarantees: Expedited parts delivery and technician dispatch for critical failures.
- Performance guarantees: Contractual commitments on fuel consumption, emissions, and noise levels with remediation if specifications aren’t met.
I’ve seen warranties become battlegrounds. A food processing plant had a generator fail at 1,900 hours (within warranty). The manufacturer claimed the failure resulted from “improper maintenance”—despite the facility following the manual to the letter and having service records proving it. The dispute dragged on for 14 months while the facility paid for rental generators. Check manufacturer reputation for warranty responsiveness before you sign.
Tools and Resources for Evaluating Manufacturers
Don’t rely on manufacturer sales materials alone. Use these resources to validate claims objectively:
Industry directories: EGSA (Electrical Generating Systems Association) and Diesel & Gas Turbine Worldwide maintain manufacturer databases and buyer’s guides.
Third-party certifications: Look for UL listing, ISO 8528 testing reports, and independent performance verification.
Competitive bidding: Create detailed RFPs requiring complete bill of materials, certified test reports, generator service network maps, pricing breakdowns, and customer references.
Site visits: Observe generators running under load at similar installations. Talk to operators about real-world performance.
Engineering consultants: For complex applications involving paralleling, renewable integration, or critical loads, professional assessment prevents costly mistakes.
How Manufacturers Fit Into Your Overall Power Strategy
Your generator exists within a broader power hierarchy: utility power (primary), UPS systems (millisecond gaps), diesel generators (extended outages), and energy storage (transients).
Your manufacturer should provide automatic transfer switches (ATS) that coordinate seamlessly with utility and UPS equipment. They should support paralleling with other generators or grid-tie configurations for on-site renewables.
Integration capabilities are crucial. Modern facilities need generators with:
- Modbus, BACnet, or SNMP protocols for building management integration
- Cloud monitoring platforms for remote diagnostics
- Demand-response system compatibility for peak shaving
Choose manufacturers whose product lines support future expansion—parallel generators, load sharing controls, and compatibility with emerging technologies like battery storage.

Best Practices for Selecting a Diesel Generator Manufacturer
Here’s the proven process I recommend:
Step 1: Define requirements – Load analysis (peak/average kW), runtime needs (standby/prime/continuous), environmental constraints, redundancy requirements, and budget.
Step 2: Pre-qualify manufacturers – Short-list 3-5 candidates with 10+ years in business, relevant certifications (ISO 8528, UL, emissions), local service networks, and positive references.
Step 3: Issue technical RFPs – Require standardized responses, site visits, and application-specific engineering (altitude derating, temperature extremes, acoustics).
Step 4: Evaluate holistically – Use weighted scoring: technical compliance (30%), total cost of ownership (25%), service capabilities (20%), reputation (15%), warranty (10%).
Step 5: Negotiate and verify – Lock in parts pricing, confirm delivery schedules with penalties, require factory testing, secure commissioning commitments.
Step 6: Plan lifecycle management – Schedule preventive maintenance, maintain service logs, exercise under load monthly, budget for major overhauls every 15,000-20,000 hours.
This process takes 4-6 months but prevents costly mistakes.
Conclusion: Making the Choice That Powers Your Future
Choosing a diesel generator manufacturer means finding a long-term partner with engineering expertise, proven components, and reliable service infrastructure.
Key takeaways:
- Reputation and track records predict future performance
- Quality engine brands (Perkins, Cummins, Volvo Penta) and alternators (Stamford, Leroy Somer) ensure reliability
- Local service networks resolve problems quickly
- Compliance (ISO 8528, NFPA 110, emissions tiers) must be straightforward
- Fuel efficiency differences create six-figure lifecycle savings
- Total cost of ownership always trumps purchase price
Companies like Tesla Power excel across these dimensions, combining proven components, comprehensive service networks, and customer-focused support—earning strong reputations in industries where failure isn’t an option.
Your facility’s power reliability depends on this decision. Take the time to do it right.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most reliable diesel generator manufacturer?
Reliability depends on your specific application, but the most reliable manufacturers share common traits: they use proven engine brands (Cummins, Perkins, Volvo Penta), partner with quality alternator makers (Stamford, Leroy Somer), maintain comprehensive service networks, and have 15+ year track records in your industry. Rather than naming a single “most reliable” brand, focus on finding manufacturers with documented success in applications similar to yours. Request case studies and reference visits to verify real-world performance.
How do I determine the right size diesel generator for my facility?
Start with a detailed load analysis. Calculate your peak electrical demand in kW, accounting for motor starting currents (which can be 5-7x running load). Add 20-25% margin for future growth and transient surges. For standby applications, you generally want a generator rated for 80-90% of peak load during normal operation. Consider whether you need prime power (extended run capability) or true standby ratings. Most manufacturers offer load calculation tools, but for critical facilities, invest in professional power systems engineering to account for harmonics, power factor, and load sequencing.
What’s the difference between prime and standby ratings for diesel generators?
Standby rating is the maximum power a generator can supply during utility outages, typically for up to 200 hours per year with maximum expected load duration of 25 hours. It represents peak capacity for emergency use. Prime rating is the maximum continuous power available with variable load for unlimited hours, typically at 80-85% of standby rating. Use prime-rated generators when grid power is unreliable or unavailable for extended periods. Standby-rated generators are appropriate for facilities with reliable utility service needing backup during rare outages. Running a standby-rated generator continuously at maximum load accelerates wear and voids warranties.
How much does a commercial diesel generator cost?
Commercial diesel generator pricing varies widely based on capacity, features, and brand. As rough guidance: 30-100 kW units run $12,000-$35,000; 100-300 kW systems cost $35,000-$90,000; 300-750 kW generators range $90,000-$250,000; and 750-2,000 kW installations run $250,000-$750,000+. These figures cover the generator set only—add 20-40% for installation (concrete pads, fuel systems, electrical connections, ATS), commissioning, and initial fueling. Remember that purchase price represents only 30-40% of total cost of ownership. Fuel consumption, maintenance, and parts over 20 years often exceed initial capital costs by 2-3x, making efficiency and reliability critical to long-term value.
What maintenance does an industrial diesel generator require?
Maintenance intensity depends on run hours, but typical schedules include: Daily/weekly (if running): visual inspections of leaks, gauges, and coolant levels. Monthly: Exercise run for 30 minutes under at least 30% load to prevent wet stacking. Every 100-250 hours or annually: oil and filter changes, fuel filter replacement, coolant checks, battery testing. Every 500-1,000 hours or 2-3 years: air filter replacement, valve adjustments, comprehensive inspection of belts, hoses, and electrical connections. Every 3,000-5,000 hours or 5-8 years: major service including injector testing, turbocharger inspection, coolant system flush. Every 15,000-20,000 hours or 15-20 years: major overhaul or engine rebuild. Keep detailed logs—warranty claims and resale value depend on documented maintenance history.
