Introduction
When your business operations depend on reliable backup power, finding the right diesel generator manufacturer isn’t just about price—it’s about trust, quality, and long-term performance. With thousands of suppliers worldwide claiming to offer “industrial-grade” equipment, how do you separate the exceptional from the mediocre?
The diesel generator market has exploded in recent years, driven by increasing power demands and more frequent grid failures. But here’s the challenge: not all manufacturers are created equal. Some prioritize cutting-edge engineering and rigorous testing, while others cut corners to compete on price alone.
I’ve spent over a decade working with power generation systems across multiple industries, from healthcare facilities that can’t afford a single second of downtime to remote mining operations where the nearest service technician is 500 miles away. Through countless installations, failures, and successes, I’ve learned what truly separates outstanding diesel generator manufacturers from the rest.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through exactly where to find reliable suppliers, what certifications actually matter (and which ones are just marketing fluff), and the critical questions you need to ask before signing any purchase order.
Understanding the Diesel Generator Manufacturing Landscape
The Global Market Structure
The diesel generator set industry operates on a tiered system. At the top, you’ll find Tier 1 manufacturers—companies like Cummins, Caterpillar, and MTU (Rolls-Royce Power Systems)—who design and manufacture both the engine and alternator in-house. These companies invest millions in research and development, maintain extensive global service networks, and stand behind their products with comprehensive warranties.
Tier 2 manufacturers typically assemble generators using engines from established producers. They might purchase a Perkins or John Deere engine, pair it with a quality alternator from Stamford or Leroy Somer, and package everything in their own enclosure. Many of these manufacturers produce excellent products, but your evaluation process becomes more complex because you’re essentially vetting multiple brands simultaneously.
Then there’s Tier 3—the assemblers who source whatever components offer the best margin at any given moment. This month’s batch might use quality parts; next month’s might not. These are the suppliers that give the industry a bad reputation.
Where Manufacturing Excellence Matters Most
Not every component requires the same level of scrutiny. The engine is your generator’s heart—this is where you absolutely cannot compromise. A substandard engine means higher fuel consumption, more frequent breakdowns, and potentially catastrophic failures at the worst possible moment.
The alternator matters almost as much. I’ve seen generators with excellent engines paired with aluminum-wound alternators that failed within 1,000 hours. Always verify 100% copper windings—the upfront cost difference is negligible compared to the replacement expense.
Control systems have evolved dramatically. Modern digital controllers from brands like ComAp or Deep Sea Electronics offer remote monitoring, predictive maintenance alerts, and seamless grid integration. But I’ve also encountered controllers so poorly programmed that they triggered nuisance shutdowns during actual emergencies.
Where to Find Reliable Diesel Generator Manufacturers
Official Manufacturer Dealer Networks
The safest starting point is always the manufacturer’s authorized dealer network. When you work with authorized dealers, you’re not just buying equipment—you’re accessing factory-trained technicians, genuine parts availability, and warranty protection that actually means something.
For Tesla Power, one of the leading names in power generation solutions, their dealer network spans across major industrial regions, providing comprehensive support from initial consultation through decades of operation. What sets authorized dealers apart is their direct access to engineering support when you encounter unusual issues.
Here’s what most people don’t realize: authorized dealers often have allocation priority during supply shortages. When a hurricane season drives demand through the roof or supply chain disruptions limit production, guess who gets their orders filled first? The authorized dealer network.
To find authorized dealers:
- Visit the manufacturer’s official website and use their dealer locator tool
- Verify the dealer’s authorization status directly with the manufacturer
- Check how long they’ve held their authorization (longer relationships typically indicate better support)
- Ask about their service capabilities—can they handle major overhauls or just routine maintenance?
Industrial Marketplaces and Directories
Several specialized platforms connect buyers with verified industrial equipment suppliers. Unlike consumer marketplaces, these platforms vet suppliers and provide detailed technical specifications.
ThomasNet remains the gold standard for North American industrial sourcing. Their supplier profiles include certifications, manufacturing capabilities, and verified customer reviews. I’ve sourced everything from portable diesel generators to 2MW industrial units through ThomasNet connections.
DirectIndustry provides global reach with particularly strong coverage in Europe and Asia. Their platform allows you to compare specifications side-by-side and request quotes from multiple suppliers simultaneously.
Global Spec focuses on engineering specifications, making it ideal when you need equipment meeting specific technical requirements. Their search filters let you narrow down suppliers by power rating, emissions compliance, and certification standards.
A word of caution: even on verified platforms, always conduct your own due diligence. Platform verification confirms a company exists and has basic credentials, but it doesn’t guarantee they’re the right fit for your specific needs.

Trade Shows and Industry Events
There’s no substitute for seeing equipment in person and meeting the people behind the brand. Major power generation trade shows bring together manufacturers, dealers, and end-users in ways that reveal company culture and commitment.
PowerGen International hosts the largest gathering of power generation professionals in North America. Walking the exhibition floor, you can physically inspect build quality, compare noise levels, and have technical conversations with factory engineers—not just sales representatives.
Middle East Electricity serves as the premier event for the Gulf region, where reliable power generation is absolutely critical. The manufacturers who invest in major presences at these shows are signaling their commitment to the market.
Smaller regional shows often provide better access to decision-makers. At a 10,000-person international show, you’re competing for attention. At a 500-person regional event, you might spend 30 minutes with a company’s chief engineer discussing your specific application.
Online Research and Vetting
The internet has made preliminary research incredibly efficient, but it’s also filled the space with misleading information. Here’s how to cut through the noise:
Start with the manufacturer’s official website, but don’t stop there. Look for technical documentation, not just marketing materials. Companies confident in their engineering publish detailed specification sheets, maintenance manuals, and application guides.
Search for independent reviews and case studies. Be skeptical of testimonials on the manufacturer’s own site—those are curated for maximum impact. Instead, look for project reports from consulting engineers, power quality studies from independent labs, and discussions in professional forums.
LinkedIn can be surprisingly valuable. Check how many employees a manufacturer has, what backgrounds their engineering team brings, and whether they’re actively posting technical content or just promotional fluff. A company with 10,000+ employees and a dedicated R&D facility in multiple countries operates differently than one with 50 employees working from a single warehouse.
Critical Quality Standards and Certifications
ISO Certifications That Actually Matter
ISO 8528 is the international standard specifically for reciprocating internal combustion engine-driven alternating current generating sets. This isn’t a generic quality management standard—it’s the technical specification that defines how generators should perform.
ISO 8528 covers multiple parts:
- Part 1: Application, ratings, and performance requirements
- Part 3: Alternating current generators
- Part 5: Generating sets (complete specification)
- Part 10: Measurement of airborne noise
When a manufacturer claims ISO 8528 compliance, ask which parts they’ve certified against. Full compliance across all relevant parts demonstrates serious commitment. Certification to just one or two parts might indicate they’re meeting minimum requirements in selected areas while cutting corners elsewhere.
ISO 9001 covers quality management systems. While important, it’s more about process consistency than technical excellence. A company can have perfect ISO 9001 processes for producing mediocre equipment. Don’t let ISO 9001 certification, by itself, convince you of superior quality.

Emissions Standards and Environmental Compliance
Emissions regulations have become increasingly stringent, and compliance isn’t optional—it’s legally mandated. Understanding these standards helps you identify manufacturers who invest in clean technology versus those trying to dump outdated inventory.
EPA Tier 4 Final represents the current standard for non-road diesel engines in the United States. Tier 4 Final engines produce 90% less particulate matter and NOx compared to Tier 2 engines. If you’re purchasing a stationary diesel generator for commercial use (not just emergency standby), Tier 4 compliance may be legally required.
The catch: Tier 4 technology adds significant cost through diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) systems, diesel particulate filters, and selective catalytic reduction. Some manufacturers offer both Tier 3 and Tier 4 models. The cheaper Tier 3 model might be legal for emergency standby use but could face restrictions for prime power applications.
Stage V serves as Europe’s equivalent to EPA Tier 4 Final. If you’re operating in the European Union, Stage V compliance isn’t optional. What’s interesting is that many global manufacturers now design to the stricter standard (Stage V) and offer those models worldwide, even where less stringent rules apply.
NFPA 110 standards govern emergency and standby power systems. While not strictly an emissions standard, NFPA 110 compliance indicates a manufacturer understands the critical nature of backup power for life safety systems. Hospitals, data centers, and emergency response facilities typically require NFPA 110 Level 1 certified equipment.
Electrical and Safety Certifications
UL 2200 certification from Underwriters Laboratories addresses fire and electrical safety for stationary engine-generator assemblies. This standard covers everything from fuel system design to electrical component safety. Many building codes require UL 2200 certification for permanently installed generators.
When Tesla Power manufactures generator sets, their UL 2200 certification isn’t just a checkbox—it represents hundreds of hours of testing and validation. The certification ensures that safety systems will function properly under fault conditions, protecting both equipment and personnel.
CSA certification is crucial for Canadian installations. While CSA and UL often harmonize their standards, explicitly verifying CSA certification avoids delays and complications with local inspectors.
For marine applications, look for ABS (American Bureau of Shipping) or Lloyd’s Register certification. Marine environments present unique challenges—salt spray, constant vibration, and limited ventilation. Marine-certified generators incorporate design features that landlubber models lack.
Key Quality Indicators When Evaluating Manufacturers
Engine Provenance and Engineering
The engine determines your generator’s fundamental reliability, efficiency, and longevity. Here’s what to investigate:
Engine manufacturer reputation: Even if you’re not buying directly from Cummins or Caterpillar, knowing these engines power the generator provides confidence. Perkins, John Deere, and Kubota also manufacture excellent industrial diesel engines. Be cautious with obscure engine brands that lack established service networks.
Displacement and operating speed: Industrial generators typically operate at 1,800 RPM (60Hz) or 1,500 RPM (50Hz). Lower-speed engines experience less wear and last significantly longer than high-speed engines. An 1,800 RPM engine will outlast a 3,600 RPM engine by a factor of two or three.
Continuous duty ratings: Manufacturers often publish multiple power ratings—standby, prime, and continuous. The standby rating represents maximum power for limited duration (typically defined as 1 hour per 12-hour period with maximum 200 hours annually). Prime rating assumes unlimited running time with a variable load averaging 70% of rated power. Continuous rating means 100% load, 24/7, indefinitely.
If your application requires running 12 hours daily, purchasing based on standby rating guarantees premature failure. You need prime or continuous rating capacity.
Alternator Quality and Technology
The alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical power. Two critical specifications demand attention:
Winding material: Insist on 100% copper windings. Aluminum conducts electricity well enough, but copper offers superior thermal performance and durability. Aluminum-wound alternators cost less upfront but rarely justify the savings when they fail prematurely.
Voltage regulation: Modern digital automatic voltage regulators (AVRs) maintain voltage within ±1% over varying loads. Older systems might drift ±5% or more, causing problems for sensitive electronics. Ask about AVR specifications and who manufactures the regulator.
Cooling system design: The alternator generates significant heat under load. Quality designs incorporate efficient cooling fans and clear airflow paths. I’ve seen budget generators where the alternator basically bakes itself because someone decided to save $50 by downsizing the cooling fan.
Control Systems and Monitoring Capabilities
Generator control technology has evolved dramatically. Modern controllers do far more than start and stop the engine.
Remote monitoring: Cloud-based monitoring systems alert you to problems before they cause failures. When a cooling system leak drops coolant levels, do you want to discover it when the engine overheats and shuts down during an emergency, or would you prefer an alert when levels first drop below normal?
Tesla Power integrates advanced monitoring across their product line, allowing facility managers to track fuel levels, maintenance schedules, and operating parameters from anywhere. This isn’t luxury—it’s practical protection for critical assets.
Automatic transfer switches (ATS): The ATS detects utility power loss and automatically starts the generator. ATS quality varies enormously. Industrial-grade ATS units from manufacturers like ASCO or Russelectric provide sub-second transfer times and decades of reliable operation. Cheap ATS units might work fine until the one time you actually need them.
Load management: Sophisticated controllers can automatically shed non-critical loads if the generator becomes overloaded, ensuring critical systems maintain power. This capability is essential for undersized installations or when you need power redundancy without oversizing equipment.
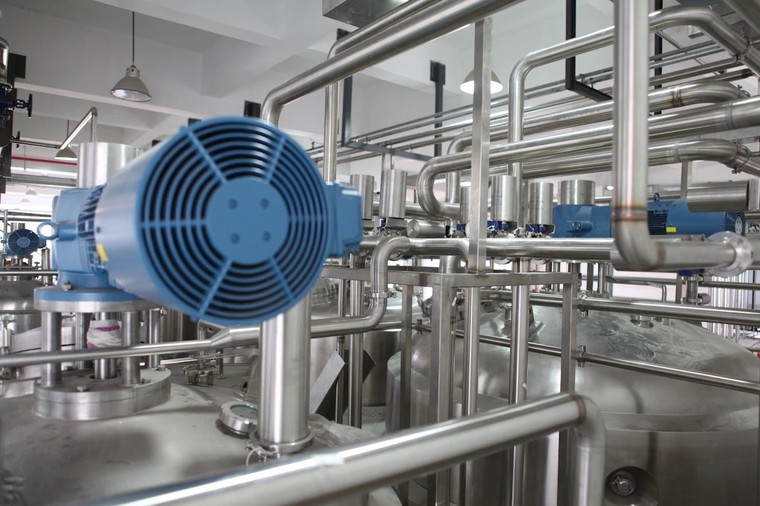
Build Quality and Enclosure Design
Examine these physical aspects:
Base frame construction: Industrial generators mount on heavy steel base frames that maintain alignment despite vibration. The base frame should incorporate vibration isolation mounts—without them, vibration gradually damages every component.
Enclosure materials: Outdoor installations require weather-resistant enclosures. Steel enclosures need proper primer and finish coats to prevent corrosion. Stainless steel costs more but may be worth it in coastal or chemical plant environments.
Sound attenuation: An open generator might produce 100+ dBA at 7 meters. Critical enclosures with proper sound attenuation can reduce this to 70 dBA. If your emergency generator sits near residential areas or in an urban environment, sound levels matter for both regulatory compliance and neighbor relations.
Fuel tank integration: Sub-base fuel tanks provide convenient fuel storage but must meet UL 142 standards for stationary tanks. Check for proper baffling (prevents fuel sloshing), adequate capacity, and easy maintenance access.

Service and Support Infrastructure
Parts Availability and Supply Chain
A generator sitting idle waiting for parts provides zero value. When evaluating manufacturers, investigate their parts distribution network.
Global parts network: Tier 1 manufacturers maintain parts distribution centers worldwide. When a fuel injector fails at 2 AM, can you get a replacement delivered by morning, or will you wait three weeks for international shipping?
Parts commonality: Some manufacturers use proprietary components for everything. Others utilize standard industrial parts wherever possible. Using standard bearings, belts, and filters means you can often source replacements locally even if the manufacturer’s parts department is backed up.
Obsolescence protection: What happens when your generator is 15 years old and needs a replacement controller? Quality manufacturers commit to parts availability for decades. Budget manufacturers might discontinue parts support after just five years.
Tesla Power maintains comprehensive parts inventories and commits to long-term parts availability, understanding that generators represent long-term investments that need ongoing support.
Technical Support and Training
The sophistication of modern generators requires trained service personnel. Evaluate the manufacturer’s support infrastructure:
Factory training programs: Do they offer formal training for service technicians? Can your maintenance staff attend courses at the factory to learn advanced diagnostics and repair techniques?
Technical support availability: When your generator throws an error code at 2 AM Saturday, can you reach a knowledgeable technician who can help troubleshoot, or does technical support work 9-5 Monday through Friday?
Documentation quality: Service manuals should provide detailed troubleshooting flowcharts, wiring diagrams, and specifications. Poor documentation turns routine maintenance into guesswork.

Making the Final Decision
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
Purchase price represents just one component of total cost. A generator that costs $50,000 but requires $10,000 annually in repairs costs far more than a $70,000 unit needing $2,000 in annual maintenance.
Factor in:
- Fuel efficiency: A generator consuming 10% less fuel than another model saves thousands annually in high-use applications
- Maintenance intervals: Extended oil change intervals reduce both parts costs and labor hours
- Downtime costs: What does an hour of lost production cost your operation? Premium reliability might justify significant upfront investment
- Resale value: Quality brands maintain value, and well-maintained units from reputable manufacturers can be resold for 40-50% of original price after a decade of service
Warranty Coverage and Terms
Read warranty terms carefully. Marketing materials might promise “5-year warranty,” but the fine print reveals important limitations:
Coverage scope: Does the warranty cover both parts and labor? Some warranties cover parts but require you to pay service labor rates.
Operating hour limitations: A “3-year warranty” might actually mean “3 years or 2,000 operating hours, whichever comes first.” For prime power applications, you might exceed hour limits long before the calendar warranty expires.
Maintenance requirements: Warranties typically require documented maintenance following manufacturer schedules. Missing even one scheduled service can void warranty coverage.
Response time commitments: What’s the manufacturer’s commitment for warranty service response? “We’ll get to it eventually” differs substantially from “48-hour response guaranteed.”
Reference Checks and Site Visits
Before committing to a major purchase, insist on speaking with existing customers operating similar equipment in similar applications. Manufacturers should readily provide references—if they hesitate, that’s a red flag.
Ask references:
- How long have you operated this equipment?
- What problems have you encountered?
- How responsive is the manufacturer’s support team?
- Would you purchase from this manufacturer again?
- What maintenance challenges have you faced?
If possible, visit an operating installation. Seeing equipment in actual service reveals things sales literature never shows.
Conclusion
Finding a reliable diesel generator manufacturer requires looking beyond glossy brochures and persuasive sales pitches. Focus on verifiable certifications, established service networks, and proven track records in applications similar to yours.
The manufacturers worth your investment demonstrate their commitment through comprehensive certifications like ISO 8528, maintain global parts distribution networks, and provide responsive technical support when you need it most. They don’t just sell you equipment—they partner with you for decades of reliable operation.
Whether you need a compact genset for occasional backup power or a multi-megawatt installation for prime power, the principles remain constant: prioritize proven engineering, insist on proper certifications, and choose manufacturers who will support your equipment throughout its entire lifecycle.
Tesla Power exemplifies these principles, combining robust engineering with comprehensive support infrastructure to deliver reliable power solutions across diverse applications. When your operations depend on continuous power, settling for anything less than the best manufacturer and support network isn’t worth the risk.
Take the time to properly evaluate manufacturers using the criteria outlined in this guide. Your future self—the one who never experiences an extended outage due to generator failure—will thank you for the diligence.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What’s the difference between a Tier 1 and Tier 2 diesel generator manufacturer?
Tier 1 manufacturers like Cummins, Caterpillar, and MTU design and build both the engine and alternator in-house, maintaining complete control over quality and performance. Tier 2 manufacturers assemble generators using engines and alternators from established suppliers. While many Tier 2 manufacturers produce excellent products, your evaluation process becomes more complex because you’re essentially vetting multiple component brands simultaneously. Tier 1 manufacturers typically offer more comprehensive warranty coverage and easier access to service support since they control the entire product.
Q2: How important are emissions certifications for diesel generators?
Emissions certifications aren’t just environmental compliance—they’re often legal requirements. EPA Tier 4 Final compliance is mandatory for many commercial diesel generator applications in the United States. Using a non-compliant generator can result in significant fines and forced shutdowns. Beyond legal requirements, modern emissions technology also improves fuel efficiency and reduces maintenance costs. Stage V compliance in Europe serves similar purposes. Always verify that your generator meets applicable emissions standards for your specific use case and location.
Q3: Should I buy directly from the manufacturer or through a dealer?
For most customers, working with an authorized dealer provides better value than direct manufacturer purchases. Authorized dealers offer local service support, faster parts availability, and established relationships with service technicians who know your area. They handle installation coordination, permitting assistance, and ongoing maintenance. Direct manufacturer purchases might save a few percentage points on initial cost but often sacrifice the convenience and support that dealers provide. The exception might be very large organizations with in-house service capabilities purchasing multiple units.
Q4: What should I look for in a generator manufacturer’s warranty?
Examine both coverage scope and practical terms. The best warranties cover both parts and labor without operating hour limitations that expire before the calendar period ends. Check maintenance requirements carefully—missing scheduled maintenance often voids coverage. Investigate response time commitments for warranty service. A warranty promising “eventual service” differs drastically from guaranteed 48-hour emergency response. Also verify whether the manufacturer or dealer handles warranty claims, as this affects service speed and convenience.
Q5: How can I verify a manufacturer’s parts availability claims?
Request specific information about parts distribution centers and inventory systems. Ask for examples of critical component delivery times to your location. Contact existing customers and ask about their parts availability experiences, especially for unexpected failures. Check whether the manufacturer maintains regional parts warehouses or ships everything from a central location. Investigate parts commonality—manufacturers using standard industrial components provide better long-term parts security than those relying entirely on proprietary parts. Request information about obsolescence protection policies for generators 10-20 years old.
